Introduction to RDBMS 🗃️
Krishna Lodha
What is RDBMS?
A Relational Database Management System (RDBMS) is software designed to store, manage, and retrieve data in a structured format using tables.
Example Table
- Storing student information in table named
student
| id | Name | Age | Gender | Class |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | John | 18 | Male | 10 |
| 2 | Jane | 18 | Female | 10 |
| 3 | Mary | 19 | Female | 10 |
| 4 | David | 20 | Male | 10 |
Example Relational Table
- Storing students marks in table as
student_marks
| student_id | subject | marks |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Maths | 80 |
| 1 | English | 90 |
| 2 | Maths | 70 |
| 2 | English | 80 |
| 3 | Maths | 90 |
| 3 | English | 80 |
Why use RDBMS?
- Efficient data storage and retrieval.
- Easy to maintain and scale.
- Supports large volumes of data.
- Ensures data integrity through constraints.
- Handles complex queries with SQL.
Core Components of RDBMS
- Tables: Structure for storing data.
- Primary Key: Unique identifier for each record.
- Foreign Key: Establishes relationships between tables.
- Indexes: Speeds up data retrieval.
- Schema: Defines database structure.
ACID Properties of RDBMS
- Atomicity: Transactions are all or nothing.
- Consistency: Always maintains valid states.
- Isolation: Transactions don’t interfere with each other.
- Durability: Changes persist after transaction completion.
Common RDBMS Software
- Open-source: MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQLite.
- Enterprise: Oracle Database, Microsoft SQL Server.
- Cloud: Amazon RDS, Google Cloud SQL, Azure SQL Database.
Demo Time!
- Let’s create a table in PostgreSQL.
- Let’s insert some data into the table.
- Let’s retrieve the data from the table.
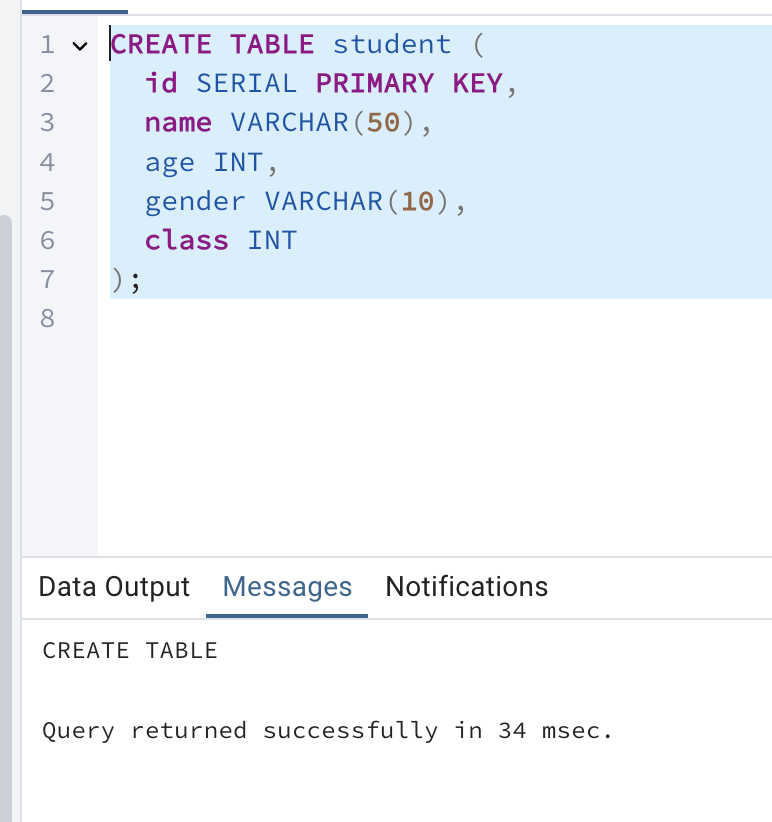
Create a table in PostgreSQL
CREATE TABLE student (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(50),
age INT,
gender VARCHAR(10),
class INT
);
create
Insert some data into the table
INSERT INTO student (name, age, gender, class)
VALUES ('John', 18, 'Male', 10),
('Jane', 18, 'Female', 10),
('Mary', 19, 'Female', 10),
('David', 20, 'Male', 10);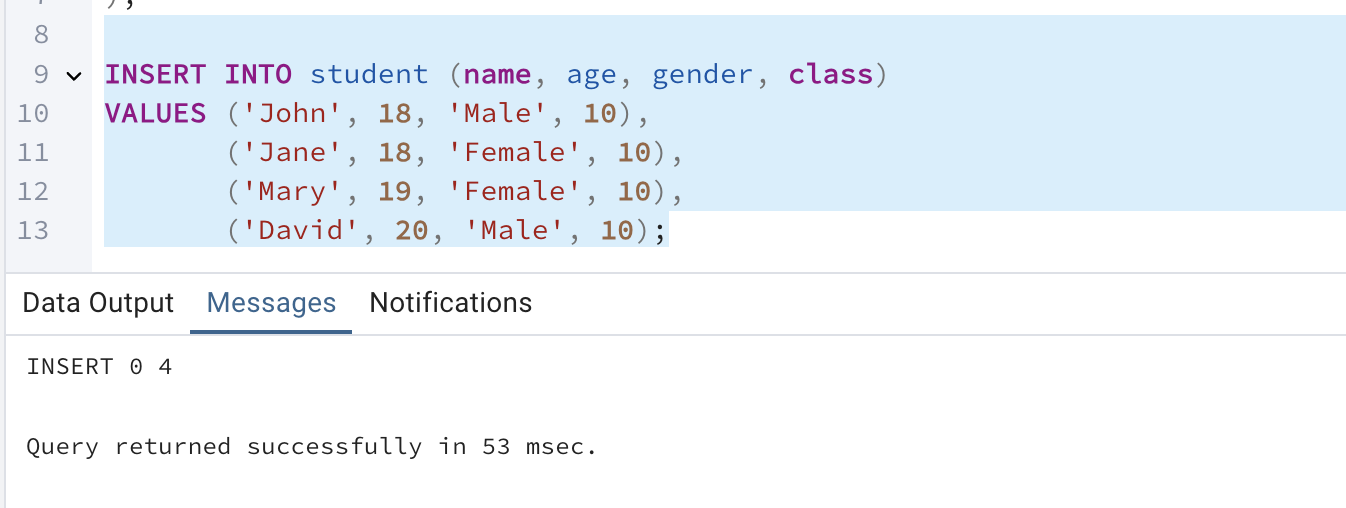
insert
Retrieve the data from the table
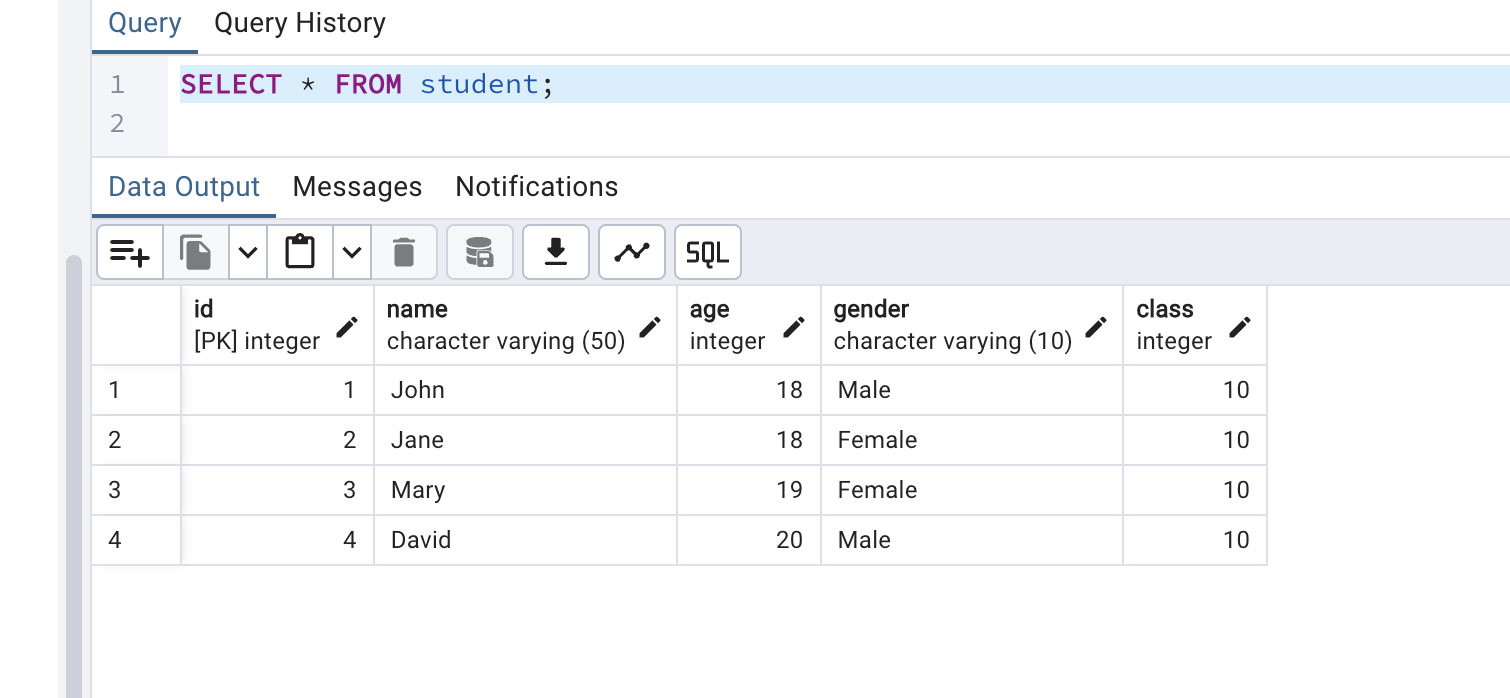
get
https://learngisonline.com/postgis/